Call us for any question
9533620200, 8179002888Meds Super Speciality Hospital
MallepallyTimings: 7 pm to 10 pm
mohammed4248asif@gmail.com
Blog s
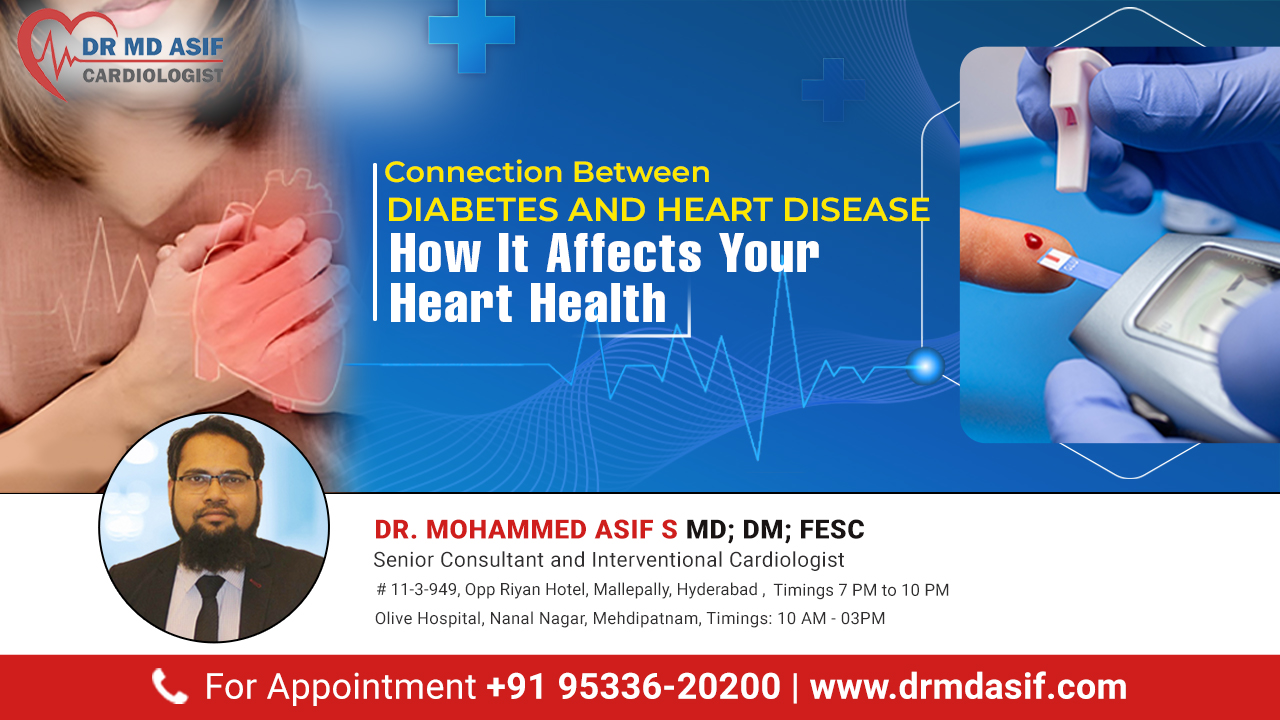
Connection Between Diabetes and Heart Disease: How It Affects Your Heart Health
Updated at: 02 Jul 2024
Introduction: Heart diseases and diabetes are two of the most common and serious health conditions globally. Even though they are frequently viewed as separate illnesses, their connection is significant, and managing one can greatly impact the health outcomes of the other. Understanding this relationship is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent heart disease. Blood Vessel Damage: High blood sugar and the nerves that control your heart. Over time, this damage can lead to atherosclerosis, where arteries become narrow and hard due to levels, typical in diabetes, which can damage blood vessel plaque buildup, restricting blood flow to the heart. Increased Blood Pressure: Diabetes often coexists with hypertension (high blood pressure), which strains the heart, damages arteries, and increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Cholesterol Levels: People with diabetes often have unhealthy cholesterol levels, including low HDL (good cholesterol) and high LDL (bad cholesterol), which contribute to artery blockage and cardiovascular complications. Obesity: Many individuals with Type 2 diabetes are overweight, which is an important risk factor for heart disease. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, increases the chance of heart disease. Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, common in diabetes, contributes to the development of cardiovascular heart diseases. Inflammation can accelerate the process of plaque buildup in the arteries, leading to heart attacks or strokes. Symptoms of Heart Diseases in Diabetic Patients: Shortness of breath Chest pain or discomfort Fatigue or weakness Nausea, vomiting, and indigestion Profuse sweating Dizziness or light-headedness Rapid or irregular heartbeat Pain in the shoulder, neck, and left arm To reduce the risk of heart disease, people with diabetes should follow these strategies: Maintain Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly monitor and control blood sugar levels with the help of medication, diet, and lifestyle changes. Healthy Eating: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods. Regular Exercise: At least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days. Walking, swimming, and cycling can improve heart health and control blood sugar levels. Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Medications may be prescribed to manage these conditions if necessary. Quit Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease and complicates diabetes management. Seek support to quit smoking for better overall health. Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to help manage diabetes and heart health. Regular Health Check-Ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider for comprehensive health check-ups can help in the early detection and management of potential complications. By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps to manage both diabetes and heart health, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of developing serious complications. Get the best cardiovascular disease treatment from Dr. Asif, the best heart specialist for all kinds of heart-related issues. FAQ: 1. How does diabetes affect heart health? Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease by damaging blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. 2. Is heart disease the leading cause of death among diabetics? Yes, heart disease is a leading cause of death and complications in people with diabetes. 3. Can diabetes-related heart disease be reversed? While some damage may be irreversible, managing diabetes effectively and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can improve heart health and reduce risks. 4. What role does medication play in preventing heart disease in diabetics? Medications for controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease in diabetics. 5. Are there specific heart diseases more common in diabetics? Diabetics are more likely to develop coronary artery disease, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy.How Diabetes Increases the Risk of Heart Disease:
Prevention Strategies:
Conclusion:
Comments

Be the first to Comment
Latest Post
-
⇨Heart Attack in the Gym: A Rising Concern
-
⇨Recognizing Early-Stage Blood Clot Symptoms in the Heart
-
⇨Obesity and Heart Disease: What is the Connection?
-
⇨Recognizing Early Signs of Prediabetes and Prevention Tips
-
⇨Impact of Chronic Rheumatic Heart Disease on Your Heart Health
-
⇨Connection Between Diabetes and Heart Disease: How It Affects Your Heart Health
-
⇨Why Regular Heart Check-ups Are Essential for Better Health
-
⇨10 ways to control high blood pressure without medication
-
⇨Know the Dos and Donts after heart bypass surgery
-
⇨Angioplasty vs CABG : All You Need to Know
-
⇨A Closer Look at Angiography Risks and Benefits
-
⇨What is the difference between angioplasty and angiogram?
-
⇨Connections Between Depression and Heart Disease: What You Need to Know
-
⇨Finding the Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad: Tips and Tricks
-
⇨How to Recognize the Signs of a Heart Attack or Heartburn
-
⇨Why Are Permanent Pacemakers Necessary, and what to expect during surgery?
-
⇨The Impact of Patent Ductus Arteriosus on Quality of Life| Dr Asif
-
⇨What Are the Causes, Risk Factors, and Treatments of Ventricular septal defect?
-
⇨Exploring the Pacemaker Surgery Cost in Hyderabad: What You Need to Know.
-
⇨Discovering the Different Types of ASD: What You Need to Know




Leave a reply